Navigating the path to voluntary sustainability reporting: An overview of the GRI standards
Navigating the path to voluntary sustainability reporting: An overview of the GRI standards
This article was published in June 2023, last updated July 2025 with information regarding GRI 102: Climate Change.
In our 2023 sustainability webinar series, Aletta Boshoff, BDO's National Leader, Sustainability, explores some popular sustainability standards, goals and frameworks while sharing insights to help organisations on their sustainability journey. Here, we highlight the key themes from our event, Sustainability spotlight: GRI Standards.
Sustainability reporting is becoming a prevalent force for driving positive change in organisations. Through the adoption of sustainability reporting, organisations not only enhance their credibility and stakeholder appeal but also showcase their commitment to sustainable development. The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) standards provide one robust and popular path to achieve this.
Here, we’ll unpack the purpose and scope of the GRI standards and explore how they empower organisations in aligning sustainability efforts with sector-specific priorities and global best practices.
While climate reporting is presently the only mandatory sustainability reporting topic for Australian entities, the GRI standards go beyond climate reporting and provide a pathway for businesses to report on their sustainability efforts across the organisation (environmental, social and governance impacts). There is interconnectedness, though, between GRI 305 Emissions and AASB S2 Climate-related Disclosures, and entities applying GRI 305 may find it easier to transition to AASB S2. However, an important difference is materiality. GRI uses a broader concept of impact materiality (i.e. the impact on the economy, environment and people, including impacts on their human rights), whereas AASB S2 focusses only on the information needs of primary users of general purpose financial reports (i.e. existing and potential investors, lenders and other creditors).
The utility of sustainability reporting for organisations
Sustainability reporting can bring a host of benefits to an organisation: by enhancing reputation, attracting stakeholders and building credibility. Sustainability reporting supports organisations to manage risks adeptly and systemically address pressing environmental and social challenges. Ultimately, the transparency and accountability that arise as a by-product of sustainability reporting serve as strong foundations for trust, and can also be a means to proactively stay ahead of regulatory requirements.
GRI Standards: Purpose and scope
The GRI Sustainability Reporting Standards, governed by the Global Sustainability Standards Board (GSSB), were first published in 2016, and are regularly reviewed to ensure they continue to reflect global best practices.
These standards offer a universally accepted structure that assists organisations in effectively gauging, managing, and communicating their governance, economic, environmental, and social impacts. By adhering to the GRI Standards, companies can disclose pertinent information consistently and transparently, enhancing comparability among different organisations and industries.
The GRI Standards encompass a wide array of environmental, social and governance (or ESG) matters, such as human rights, labour practices, biodiversity, energy and emissions. This comprehensive, all-encompassing approach ensures that businesses can evaluate and report on all significant facets of their sustainability performance.
Significantly, the GRI Standards are intended to be applicable to organisations of varying sizes and industries. Whether an organisation is a small local business or a multinational corporation, the GRI Standards offer a flexible framework that can be customised to fulfil specific reporting requirements. This inclusiveness enables companies across diverse sectors to participate in sustainability reporting and contribute to a more environmentally friendly and accountable future.
Implementation of the GRI Standards
To effectively implement the GRI Standards, businesses must establish a robust framework, taking into account the following factors.
Conducting a materiality assessment
When implementing GRI Standards, organisations will begin by conducting a materiality assessment. This process helps to identify the most relevant sustainability topics for the organisation to report, based on the significance of economic, environmental and social impacts. By focusing on material issues that affect stakeholders and long-term environmental performance, businesses ensure their reporting is targeted and meaningful.
Stakeholder engagement and alignment
Engaging stakeholders is a fundamental step in aligning with the GRI Standards. Organisations should actively involve employees, customers, investors, and communities to understand their sustainability expectations, concerns, and priorities. This engagement ensures that reporting addresses stakeholders’ information needs and reflects their perspectives.
Promoting transparency and accountability
Transparency is a cardinal principle of GRI Standards implementation. To build trust among stakeholders and enable informed decision-making, companies disclose accurate and comprehensive information about their sustainability performance, goals and progress.
Structure of the GRI Standards
The modular structure provided by the GRI Standards has emerged as the gold standard for sustainability reporting. It provides a robust framework that guides organisations towards comprehensive and relevant reporting.
Under the GRI structure, Standards are categorised into three buckets, being:
- Universal Standards – three areas of general disclosure that all organisations need to apply to their reporting
- Sector Standards – particular standards addressing issues identified by the broader industry
- Topic Standards – supports adequate reporting on the topics identified as material to the organisation.
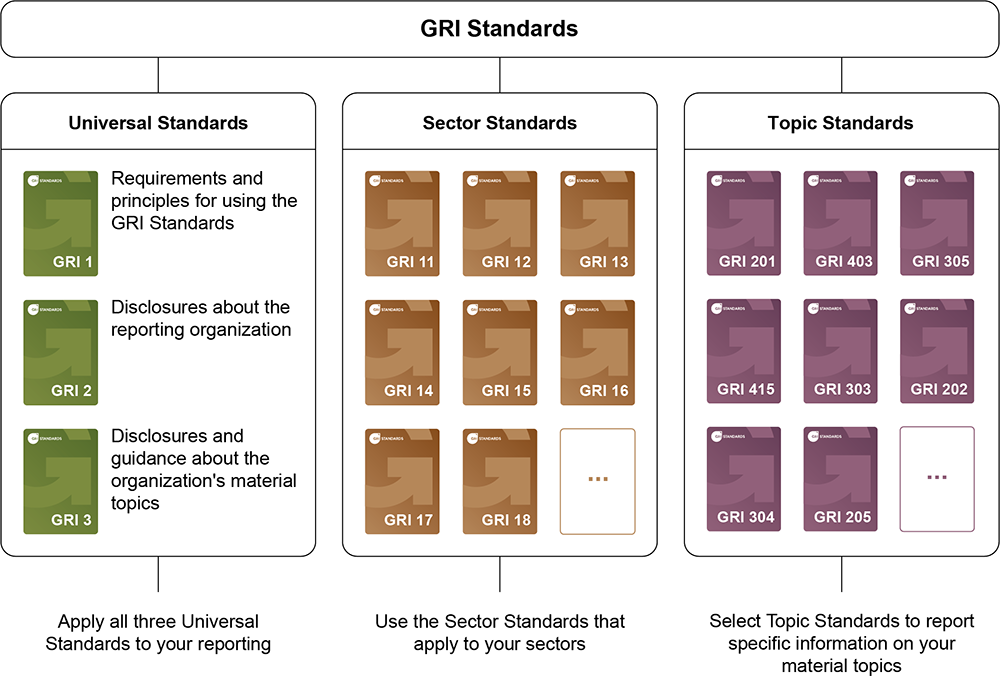
Figure 1 – GRI Standards’ modular system of interconnected standards
Sustainability reporting varies across industries, considering each sectors’ unique challenges and impacts. Based on these considerations, businesses must identify and prioritise relevant sustainability topics. For example, the energy industry may focus on carbon emissions, while the manufacturing industry may prioritise labour practices, and the agricultural sector may emphasise water management.
The GRI Standards recognise the sector-specific nature of sustainability reporting. They provide guidance on sector-specific disclosures and indicators, ensuring comprehensive coverage of topics across industries. Companies can effectively address their sustainability impacts and contribute to industry-wide progress by tailoring reporting to industry-specific challenges.
However, we know that not all organisations are identical, even within a sector. So, organisations must also address sustainability issues that are pertinent to them and their stakeholders. The Topic Standards enable the disclosure of non-industry-specific issues as identified through the materiality assessment.
Other considerations when implementing the GRI Standards
Once the relevant standards have been identified for reporting, organisations also need to consider the specific disclosures and structure of the report, including:
- Core and comprehensive options: GRI Standards offer organisations the choice between:
- Core reporting - covering minimal reporting requirements to understand the nature of the organisation, material topics and related effects, or
- Comprehensive reporting - including additional disclosures for more extensive reporting on areas such as strategy, ethics and integrity, or governance.
- Sections and components: The standards are organised into different sections, including economic performance, environmental impact, social practices and governance. Each section comprises specific components and indicators that guide businesses in measuring and reporting on their performance in these areas.
- Materiality assessment: The process of choosing and revealing pertinent subjects through careful evaluation. This evaluation aids in recognising sustainability concerns that possess a substantial influence on both the organisation and its stakeholders. Consequently, it guarantees that reporting concentrates on the most crucial areas.
By offering organisations the flexibility to choose between the core and comprehensive options, the GRI Standards allow for the diverse reporting needs of different entities. This adaptability enables an organisation to tailor its sustainability report based on its specific priorities and the expectations of its stakeholders. The structured nature of the GRI Standards, with its sections, components, topics and sectors, ensures that no vital aspect of sustainability performance is overlooked, thus instilling confidence in the credibility and transparency of the reported information.
Notably, the GRI Standards also align with other frameworks and initiatives, such as, the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals, Taskforce for Climate-related Financial Disclosures, and SASB Standards, among others.
Latest updates to GRI standards
GRI 101: Biodiversity standard
In January 2024, GRI updated their biodiversity standard (GRI 101), with the main changes including:
- Facilitating reporting of impacts on biodiversity across the supply chain - requires information about products and services in the supply chain that have the most significant impacts on biodiversity, as well as recommendations for disclosing information about the downstream value chain if this is available
- Clarifying that information is only required about the most significant impacts
- New disclosures about how the organisation determines which sites and which products and services in the supply chain have the most significant actual and potential impacts on biodiversity
- An emphasis on providing location-specific impacts
- New disclosures about the direct drivers of biodiversity loss: land and sea use change, exploitation of natural resources, pollution and invasive alien species
- New disclosures about the changes to the state of biodiversity, including the type, size and conditions of ecosystems affected or potentially affected
- New requirements on the impacts on people resulting from the organisation’s impact on biodiversity
- New biodiversity-specific management disclosures regarding the organisation’s policies and commitment to halt and reduce biodiversity loss.
The updated standard will be effective on 1 January 2026, but early adoption is encouraged.
In June 2025, the GRI expanded its framework with the release of two new standards, GRI 102: Climate Change and GRI 103: Energy. These standards are designed to help organisations disclose their climate-related and energy impacts and demonstrate how they are being managed in alignment with global sustainability goals.
GRI 102: Climate Change
Key features of the new standard:
- Introduces disclosures on just transition principles, including impacts on workers, communities, and vulnerable groups.
- Requires reporting on transition plans, including alignment with scientific evidence and fossil fuel phase-out targets.
- Adds disclosures on GHG removals, carbon credits, and climate adaptation plans.
This new standard also supports interoperability with other major frameworks, including the IFRS S2 Climate-related Disclosures standard, particularly around Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions. This alignment helps organisations streamline reporting and more efficiently meet multiple stakeholder and regulatory expectations.
GRI 103: Energy
Key features of the new standard:
- Focuses on energy consumption, efficiency, and renewable sourcing.
- Requires disclosures on energy policies, target setting, and value chain impacts.
- Emphasises the role of energy in transitioning to a decarbonised economy.
These standards deepen the environmental and social components of sustainability reporting, reinforce alignment with global climate goals and regulatory expectations, and provide clearer guidance on climate risks, energy use, and transition planning.
Guidance along your sustainability report journey
Ready to take steps toward addressing your carbon footprint in your sustainability report? Our sustainability reporting team is here to provide expert guidance. With our in-depth knowledge of sustainability practices, we can assist your business in developing its sustainability report.
Contact us today to explore how we can help you navigate the complexities of sustainability reporting, ensuring that your efforts are impactful and aligned with industry best practices.
