GHG Protocol - Measuring downstream Scope 3 emissions
GHG Protocol - Measuring downstream Scope 3 emissions
In the second half of 2023, our sustainability webinar series walks step-by-step through the GHG Protocol. Aletta Boshoff and Dylan Byrne summarise the key messages from our November webinar, which explains how to measure downstream Scope 3 emissions.
What are Scope 3 emissions?
Scope 3 emissions are indirect emissions that do not arise from an entity’s Scope 2 emissions (purchased electricity, steam, heating and cooling for own use). They relate to the entity’s upstream activities if the entity reports emissions on a ‘cradle-to-gate’ basis, and also downstream activities if the entity reports on a ‘cradle-to-grave’ basis. There are fifteen Scope 3 categories, shown in the diagram below.
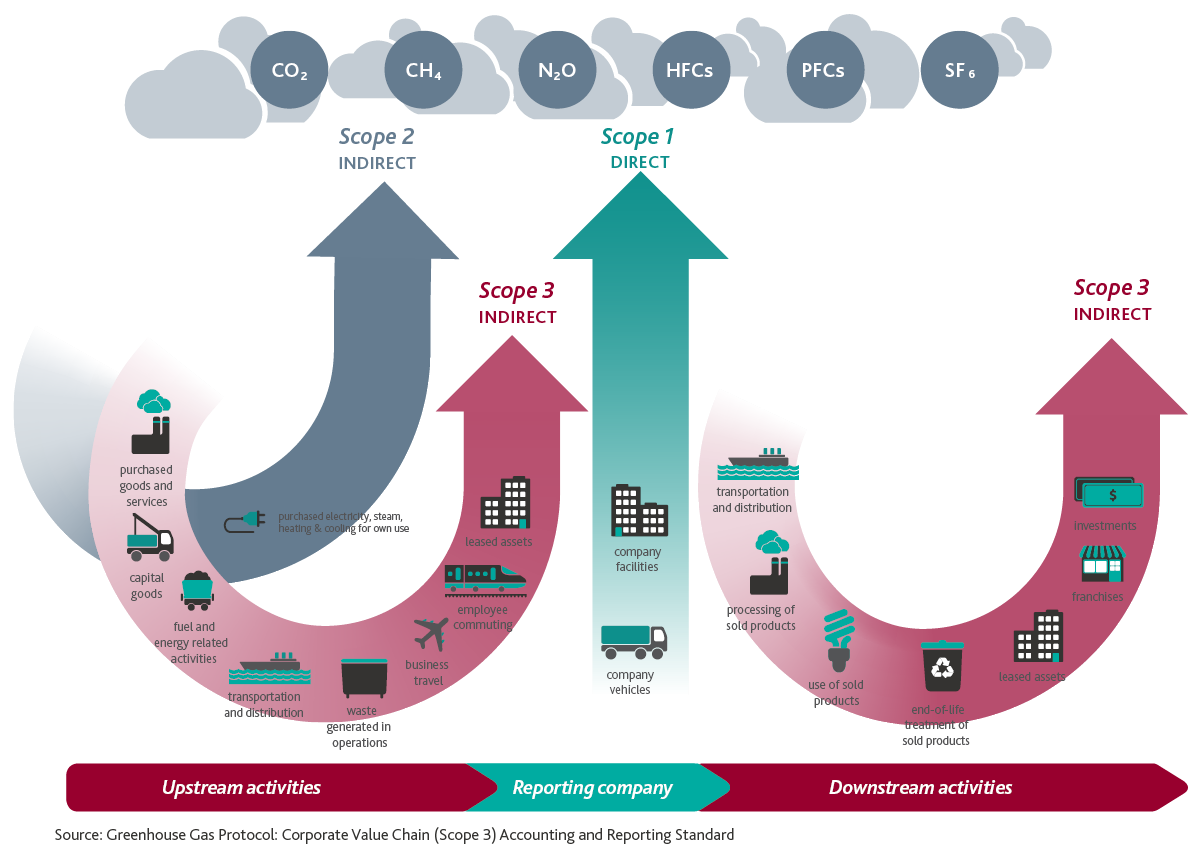
Collecting Scope 3 data for downstream emissions
Scope 3 emissions cannot be measured unless data is collected for all of the fifteen categories in the diagram above. During the webinar, we focussed on collecting data for the seven categories of Scope 3 emissions which relate to an entity’s downstream activities. Last month’s webinar discussed how data is collected for upstream activities.
|
|
Category |
Description (extracted from Table [5.4] in the Corporate Value Chain (Scope 3) Accounting and Reporting Standard) |
Examples of primary and secondary data (extracted from Table [7.4] in the Corporate Value Chain (Scope 3) Accounting and Reporting Standard) |
|
9 |
Downstream transportation and distribution of sold goods |
Transportation and distribution of products sold by the reporting company in the reporting year between the reporting company’s operations and the end consumer (if not paid for by the reporting company), including retail and storage (in vehicles and facilities not owned or controlled by the reporting company) Notes:
|
Primary data
Secondary data
|
|
10 |
Processing of sold products |
Processing of intermediate products sold in the reporting year by downstream companies (e.g., manufacturers) |
Primary data
Secondary data
|
|
11 |
Use of sold products |
End use of goods and services sold by the reporting company in the reporting year Notes:
|
Primary data
Secondary data
|
|
12 |
End-of-life treatment of sold products |
Waste disposal and treatment of products sold by the reporting company (in the reporting year) at the end of their life Notes:
|
Primary data
Secondary data
|
|
13 |
Downstream leased assets |
Operation of assets owned by the reporting company (lessor) and leased to other entities in the reporting year, not included in Scope 1 and Scope 2 – reported by lessor Notes:
|
Primary data
Secondary data
|
|
14 |
Franchises |
Operation of franchises in the reporting year, not included in Scope 1 and Scope 2 – reported by franchisor Note: Franchisors should account for emissions that occur from operations of the franchises (i.e. the Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions of franchisees). |
Primary data
Secondary data
|
|
15 |
Investments |
Operation of investments (including equity and debt investments and project finance) in the reporting year, not included in Scope 1 or Scope 2 Notes:
|
Primary data
Secondary data
|
Importance of engaging with your suppliers and customers
Entities need to engage with suppliers and customers throughout the supply chain to obtain the data necessary to calculate Scope 3 emissions. While industry averages (secondary data) may be readily available, this may often result in higher Scope 3 emissions than if primary data were used. It is therefore important that entities engage with suppliers (for Scope 3 upstream emissions) and customers (for Scope 3 downstream emissions) in order to obtain more precise and accurate primary data. An added benefit is that this engagement is likely to speed up the process of carbon emission reduction across the supply chain.
Want to understand more about the GHG Protocol?
You can find more information about measuring Scope 3 GHG emissions in the Corporate Value Chain (Scope 3) Accounting and Reporting Standard and the Technical Guidance for Calculating Scope 3 Emissions.
You can also register now for more events in BDO's 2024 sustainability webinar series.
If you need a hand in identifying and measuring your Scope 3 emissions, our national sustainability team can help. Contact us today.